Django 체험하기
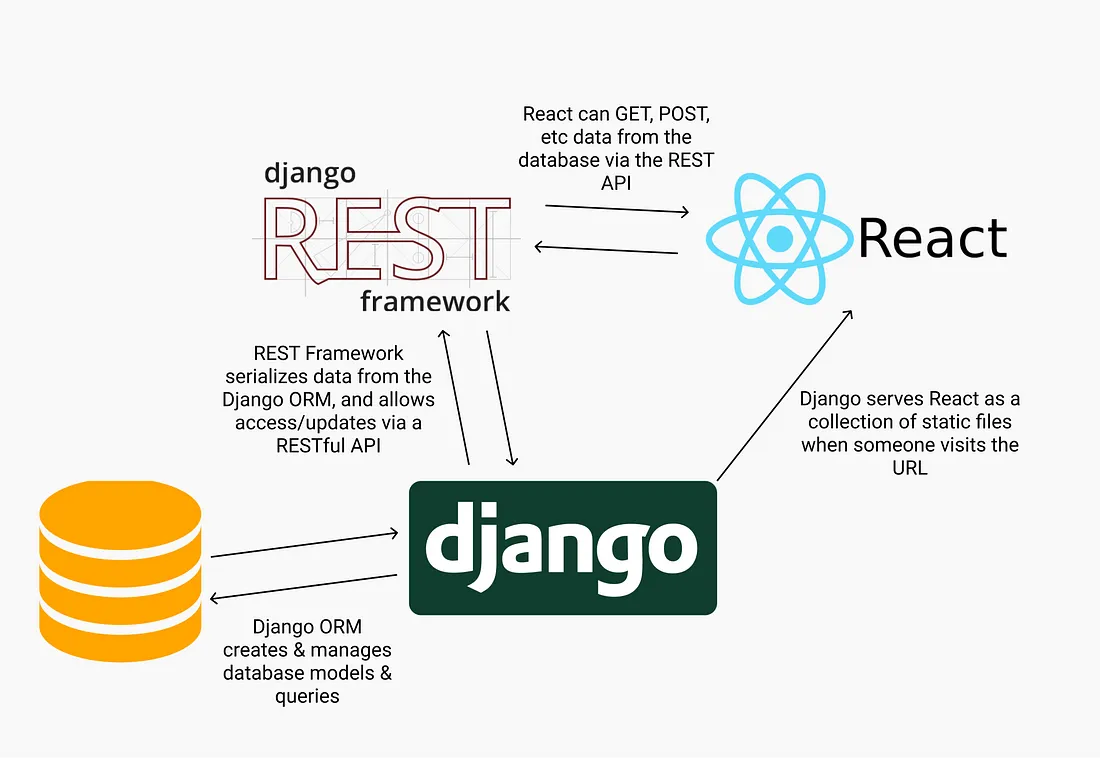
django의 역할
- backend에서 쓰이는 framework
web server - was - db의 3-tier architecture를 구성해보자.
정적인 contents(사용자의 요청과 관계없이 동일한 내용을 출력)를 담당할 web server를 만들기 위해 react framework를 활용한다.
동적인 contents(사용자의 요청에 따라 달라지는 내용을 출력)를 처리하는 was에서는 rest api를 통해 web server와 통신하는데, rest api 통신을 위해 django rest framework를 활용하고, contents를 처리 하기 위해 django framework를 활용한다.
Data를 적재할 DB는 open source db 중 하나인 mariadb를 활용한다.
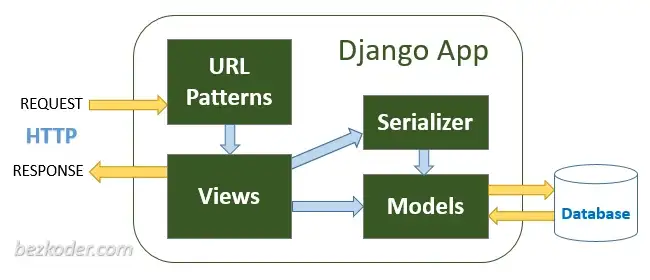
django 구조 이해하기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
project/
manage.py
project/
__init__.py
settings.py
urls.py
asgi.py
wsgi.py
app/
__init__.py
admin.py
apps.py
migrations/
__init__.py
models.py
tests.py
views.py
manage.py: 이 file을 통해 django project와 상호작용할 수 있는 명령어를 내릴 수 있다. project/: project를 위한 실제 python package들이 저장된다. project/init.py: 이 project가 python package라는 것을 선언하는 file project/settings.py: 이 project의 환경 설정을 저장한다. project/urls.py: 이 project의 url 경로들을 저장한다. include를 통해 여러 app으로 향하는 경로를 저장할 수 있다.
ex)app/urls.py의 url을 참조하기 위해서는 project/urls.py에 path('app/', include('app.urls))를 urlpatterns에 추가해야 한다.+ python manage.py check로 project의 문제를 확인할 수 있다.
app/urls.py: app의 세부 경로들이 app/views.py의 어떤 view 또는 함수와 연관되는 것인지를 저장한다. app/models.py: db table을 생성하기 위해 model들을 정의한다.
- migrate: setting.py 안의 INSTALLED_APPS의 설정에 따라 DB table을 만든다.
- makemigrations: models의 변경사항을 migration으로 저장한다고 선언한다.
- sqlmigrate: migration 이름을 인수로 받아 실행한다.
- showmigrations: migration 상태를 보여준다.
- models.py에 객체를 생성했으면 이 앱을 project에 추가하기 위해, settings.py 안의 INSTALLED_APPS 설정에 추가해야 한다.
이후 makemigrations를 실행시켜서, model을 변경시킨 사실을 migration file로 만들고 migrate를 통해 변경사항을 적용시킨다. app/views.py: HttpResponse 객체를 반환하거나, 혹은 Http404 같은 예외를 발생시킨다. app/urls.py와 연동된 url에서 나타낼 화면의내용이 들어간다. 해당 url에서 어떤 html file을 출력할 것인지 또는 어떤 처리를 할 것인지를 정의한다. app/templates/: app/views.py와 연동되어 화면에 출력될 html file들을 저장한다. app/admin.py: app/models.py에서 정의된 model들을 admin page에서 CRUD가 가능하도록 권한을 부여한다.
model 만들기
models.py file을 다음과 같이 구성한다. 각 class는 db table을 만든다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from django.db import models
class Question(models.Model):
question_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = models.DateTimeField('date published')
class Choice(models.Model):
question = models.ForeignKey(Question, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
choice_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
votes = models.IntegerField(default=0)
primary key(pk)는 자동으로 추가된다. (자동으로 추가하지 않도록 수정할 수 있다.) django는 foreign key 이름에 “_id”를 자동으로 추가한다. (수정 가능)
View 만들기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template import loader
from .models import Question
def index(request):
latest_question_list = Question.objects.order_by('-pub_date')[:5]
template = loader.get_template('polls/index.html')
context = {
'latest_question_list': latest_question_list,
}
return HttpResponse(template.render(context, request))
polls/index.html template을 불러온 후, context를 전달한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
from django.shortcuts import render
from .models import Question
def index(request):
latest_question_list = Question.objects.order_by('-pub_date')[:5]
context = {'latest_question_list': latest_question_list}
return render(request, 'polls/index.html', context)
render() 함수를 통해 코드의 크기를 좀 더 줄일 수 있다.
Generic View 만들기
function 기반의 view에 비해 class 기반의 view는 가독성을 높일 수 있고, Mixin과 같은 tool을 활용함으로써 유연성 또한 높일 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404, render
from django.urls import reverse
from django.views import generic
from .models import Choice, Question
class IndexView(generic.ListView):
template_name = 'polls/index.html'
context_object_name = 'latest_question_list'
def get_queryset(self):
"""Return the last five published questions."""
return Question.objects.order_by('-pub_date')[:5]
class DetailView(generic.DetailView):
model = Question
template_name = 'polls/detail.html'
class ResultsView(generic.DetailView):
model = Question
template_name = 'polls/results.html'
이 tutorial에서 중요한 부분은 django가 backend용 framework로 DB와 통신하는 것이 주요 기능이기 때문에, model, view 쪽의 data를 어떻게 처리하는 것인지, 과정에 대해 중점적으로 고민해봐야겠다. 더불어 tutorial에는 없지만 middleware 쪽도 더 탐구해봐야겠다.
참고
- https://www.w3schools.com/django/index.php
- https://docs.djangoproject.com/ko/4.0/intro/tutorial01/
- https://bennettgarner.medium.com/react-on-django-getting-started-f30de8d23504
- https://blog.toycrane.xyz/web-was-%EC%84%9C%EB%B2%84%EC%97%90-%EB%8C%80%ED%95%B4-%EC%95%8C%EC%95%84%EB%B3%B4%EC%9E%90-34861e69ac4e
- https://mahdiaaliyya.medium.com/software-architecture-bb44325bf0cf